Cold chain logistics: a complete guide
 By
Giulia Castagna
·
4 minute read
By
Giulia Castagna
·
4 minute read

The transportation of perishable goods is governed by strict regulations across the globe. This is due to the numerous risks associated with improper storage, which can often be detrimental to health. Hence, the cold chain was established to ensure the quality of food products.In this article, we will explore the entire process of transporting and storing fresh and frozen products. We will also examine best practices to optimise the cold chain and look at some of the carriers that offer services for transporting these consumer goods.
Cold chain: what is it?

The cold chain is a logistical process that maintains a constant and controlled temperature for perishable food products, from production to distribution.
This system is essential to prevent the growth of microorganisms, maintain the food safety standards required by current regulations, and ensure that products retain their organoleptic and nutritional properties until they reach the end consumer.
Cold chain regulations: a legislative overview
Discussing cold chain regulations without mentioning HACCP is impossible. Initially developed as a protocol for managing food supplies for NASA's space missions, HACCP was introduced in Europe in the 1970s and then incorporated into Regulation (EC) No 852/2004, which sets out general hygiene rules for food products.
In the UK, the Food Safety and Hygiene (England) Regulations 2013 and subsequent regulations align with these principles and introduce specific measures. These regulations require food businesses to:
- Keep food below 8°C in order to “inhibit or prevent harmful micro organisms from multiplying”
- Monitor and record temperature at all times
- Isolate high-risk foods
And much more, of course.
Since 2006, the HACCP protocol has also been applied to businesses trading in pet food, not just human food.
HACCP: 7 principles
The HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) protocol involves 7 principles, which are as follows:
- Hazard identification and risk analysis
- Identification of CCPs (Critical Control Points)
- Establishment of critical limits
- Establishment of monitoring procedures
- Establishment and planning of corrective actions
- Establishment of verification procedures
- Establishment of record-keeping procedures
Key challenges in the cold chain for food companies
1. Cold chain breaks
A break of the cold chain refers to any lapse in maintaining the constant temperature required for product preservation. This is a major issue in food logistics, potentially rendering goods unsellable or causing them to degrade more quickly, leading to financial losses for businesses.
Breaks can occur at any point in the cold chain, from storage to transport, and during the critical stages of loading and unloading trucks.
2. Cost reduction
Maintaining the cold chain requires significant investment in refrigeration equipment, energy, and staff training. This can be a challenge, especially for SMEs that may lack the resources for advanced temperature monitoring and control systems.
However, adopting innovative technologies can pay off over time by reducing energy consumption and operational costs, thus effectively lowering cold chain management expenses. If the financial barrier remains insurmountable, businesses can partner with logistics providers to outsource their food logistics operations.
3. Regulatory compliance
Ensuring all operations comply with current regulations requires continuous monitoring and regular updates to business procedures.
Collaborating with legal experts and attending training courses can help maintain high compliance standards. The adoption of compliance management software can simplify monitoring and documentation, ensuring that all operations meet the current regulations.
Best practices for cold chain management
1. Continuous temperature monitoring
A temperature monitoring system not only records data but also provides predictive analysis and detailed reports.
The adoption of advanced IoT solutions enables the integration of smart sensors that monitor in real time and predict potential issues through historical data analysis. This proactivity is crucial to prevent cold chain breaks.
A good monitoring system should integrate seamlessly with business management systems (ERP) for centralised and efficient control.
2. Active and smart packaging solutions
Beyond selecting insulating packaging, it's important to invest in active packaging technologies (such as those that absorb oxygen in the box) that use phase change materials (PCM) to maintain a constant temperature for longer.
Active packaging solutions not only extend shelf life but also reduce the need for frequent checks.
At the same time, transport vehicles should be equipped with refrigeration systems that can activate in case of a main system failure, ensuring an uninterrupted cold chain.
3. Staff training
Ongoing staff training, aside from being a legal requirement, can improve responsiveness and readiness in critical situations.
Furthermore, incentivising staff with certification programmes can lead to stricter adherence to cold chain management procedures and quicker adoption of new technologies within the company.
4. Logistics planning
Logistics planning should integrate advanced route optimisation tools that consider not only distance but also real-time traffic conditions, weather conditions, and refrigerated rest points along the route.
Implementing logistics management software that offers end-to-end shipment visibility enables informed and timely decision-making, minimising the risks of cold chain breaks.
5. Using blockchain technology for traceability
Blockchain technology offers solutions to enhance transparency and traceability in the cold chain.
Integrating blockchain into business processes allows for recording every stage of the supply chain, thus enabling monitoring and verification of all steps.
In the event of issues, blockchain simplifies identifying the exact point where the error occurred, improving emergency response efficiency.
6. Vehicle load optimisation
Optimising vehicle loads is another crucial aspect. Unbalanced loads can compromise the efficiency of the refrigeration system.
Using load optimisation software can help distribute weight evenly, improving temperature stability during transport.
Such software can also suggest loading and unloading orders to reduce the time vehicle doors are open, minimising temperature fluctuations and optimising delivery operations.
Carrier services for cold chain
BRT Fresh
BRT Fresh is BRT's service dedicated to temperature-controlled transport (between 0°C and 4°C) for fresh food products (excluding frozen goods). This service offers:
- Single-parcel shipments up to 31.5kg and 85x45x50 cm in size.
- Expiry date management with a block for products past their expiry (thus preventing the shipment of unsellable food).
- Distribution block in case of product recall.
- Two delivery attempts and the option for delivery to the floor.
Stef
Stef is a European specialist in temperature-controlled transport for agri-food products. Their services include:
- Transport of temperature-controlled goods nationally, across Europe, and internationally.
- Transport of frozen, fresh, and temperature-sensitive foods.
- Delivery to airport warehouses with included porterage service.
Chronofresh® (by Chronopost)
Chronofresh® is the temperature-controlled transport service of the French giant Chronopost. The carrier allows for managing the cold chain for both fresh and frozen products. The service features:
- Parcel handling up to 30kg and dimensions of L60 x W40 x H40.
- Next-day delivery for domestic shipments within France. Cross-border to Belgium and Spain within 2 business days.
- Transport for ambient products available across Europe, French overseas territories, and the rest of the world.
- Expiry date management with a block for products past their expiry (thus preventing the delivery of unsellable or inedible food).
- Distribution block in case of product recall.
- Two delivery attempts and the option for delivery to the customer's door, whether B2B or B2C.
Optimise your cold chain logistics with ShippyPro
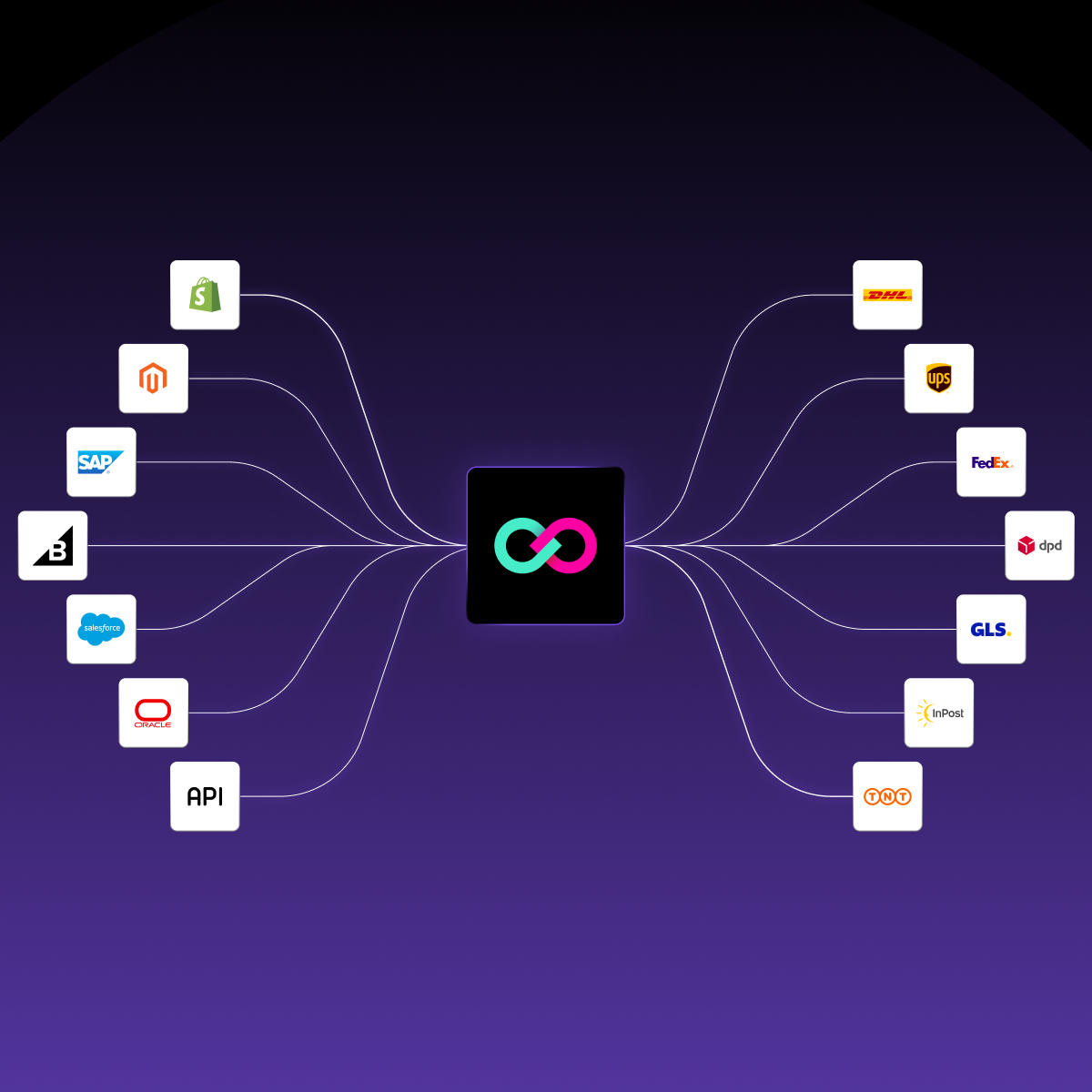
ShippyPro is a logistics platform that allows you to integrate over +1300 carrier services for food into your technology stack in just a few steps.
Among the suite's services specific to optimising food logistics are:
-
- Multi-carrier shipping management: selecting the most cost-effective rates, automating, and standardising labels.
- Paperless documentation to reduce costs.
- Monitoring all shipments from a single platform.
- Retrieval of PODs.
- Validation of delivery addresses to avoid any mode of error and goods in storage.
- Analysis of courier invoices to identify discrepancies and extra charges.

Curious by nature, analytical by mindset, Giulia Castagna is the voice behind ShippyPro’s content. As Content Marketing Manager, she simplifies complex logistics topics for those who ship around the world every day. She writes about AI, automation, and shipping trends to inspire data-driven decisions.