Headless commerce: what it is, advantages and the 8 main platforms

The world of online sales shows no sign of stopping its evolution and the latest ecommerce trend is represented by headless commerce.
This new way of structuring online sales is revolutionising ecommerce and digital marketing, focusing, even more than in the past, on the customer's experience and the product journey, all thanks to the use of new technologies.
In this article we will discover what headless commerce is, the differences with traditional ecommerce, the advantages and disadvantages, as well as the best platforms that allow you to explore these new sales opportunities.
Headless commerce: meaning
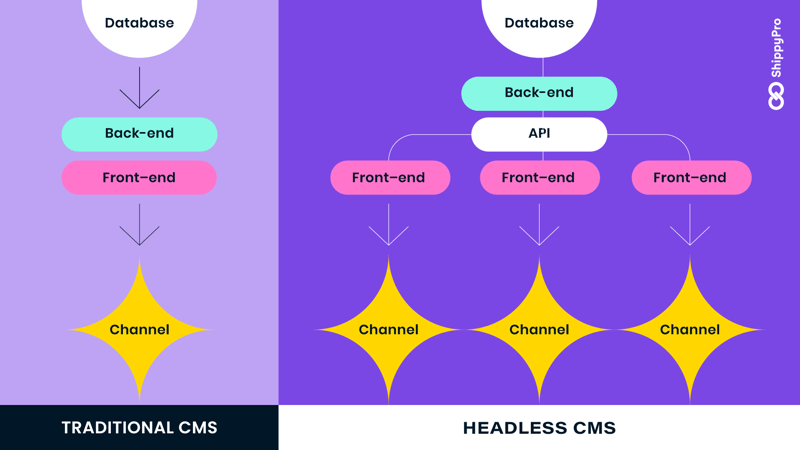
This type of architecture separates the front end of the online store (the "head" of the e-commerce) or the part that the customer views and interacts with, from the back end, namely the section related to product management and infrastructure programming.
The back end of an ecommerce website is where all the product data sheets, features, prices, etc. are stored. It allows you to manage the entire ecommerce and to control the section that is accessible to visitors, i.e., the front end, the user interface.
Well, if so far with traditional technology these two realities were united and directly connected, with headless commerce it is possible to separate them.
With this technology, you can use any front-end interface, such as a website or mobile app, to access online store data and functionalities via API (application programming interface), a programmable system used to exchange information between software.
This means that customers, for example, will be able to complete transactions from any of the touchpoints where they viewed the product and enjoy a faster and more personalised shopping experience. Programmers, on the other hand, will be able to work on the back end using the programming language that is most familiar to them, without constraints related to the use of templates or the risk of causing problems to the user experience.
In general, the transition to headless commerce strengthens the entire company structure, making all operations more agile, faster, and leaner, including logistics.
However, to fully comprehend how this new way of understanding electronic commerce works, it is necessary to take a step back and learn more about how traditional ecommerce works.
How traditional ecommerce works
In traditional ecommerce, the dualism of back and front is unvaried. Back end is the database where all the functions and processes for the display and sale of products are collected, with their characteristics, shipping methods, discounts etc.
The front end, on the other hand, is the ecommerce site we all see, namely the user interface. It is the contact point between the customer and the site, which allows those who want to buy a product to view and place an order.
The customer interacts with the ecommerce site following a customer journey and touchpoints.
The customer journey is the path that customers take from the moment they come into contact with the brand to the moment they purchase something. It can have different phases such as product discovery, option evaluation, and purchase decision.
Touchpoints are contact points, i.e., the points where the consumer interacts with the brand. An example can be visiting the website, a click on a social profile or an email.
This means that the customer journey has a series of touchpoints that culminate in the purchase of the product.
In traditional ecommerce, regardless of the online marketing strategy used by a company, at each touchpoint customers will always be directed to the original website to complete the purchase or will be forced to leave the platform they are currently using (Facebook, Instagram, email) and go to the brand's website.
In this way there are a series of obligatory steps to take, which depend on the site's architecture, the template, the shopping cart, and the payment system... a series of constraints that do not allow much room for customization and innovation.
From the customer's perspective, this can be a slowdown, a moment in which they could question their purchase, thus increasing the abandoned cart rate. In short, the longer and more complex these steps are, the more the conversion rate is reduced.
How does headless ecommerce work?
With headless commerce, the brand can adapt the various touchpoints along the customer journey more easily. Being able to separate the front end from the back end allows more creative freedom and greater compatibility with each channel on which the products are displayed, such as social networks, blogs, or the website itself.

This compatibility is possible thanks to APIs. More specifically, the back end communicates with the front end through this information exchange system, without employing directly connected code. This means you can work freely in the management system and make the various changes along the contact points automatically, even outside the site itself.
In headless commerce, APIs therefore allow the front end to communicate with the back end in a direct way. The changes to the information and functions are made only once, in the back end, and all the front ends that have been created are updated automatically. Moreover, you always have direct access to those changes. And vice versa, each front end can be modified independently, without affecting the back end. This allows greater freedom, since you are no longer forced to adapt to templates or employ pre-set customizations that can limit your creativity, but you can finally implement any innovation and test you like.
In this way, customers will be able to find a coherent sales experience throughout the customer journey, from the smartphone app or smartwatch to social networks, and make their purchases from any touchpoint without having to leave the platform they are using.
For example, Michael Kors is a luxury brand that switched to this technology in 2016 to solve the problems connected to having their site hosted separately on desktop and mobile. This made the update process difficult and inefficient, since they were dealing with dozens of different sites, languages, and currencies. The transition to a headless system allowed them to create a single backend for all the online presences of the brand and update each touchpoint automatically via API.
Advantages and disadvantages of headless commerce

Headless commerce has several advantages. Let’s discover the most important ones.
- Flexibility: with headless commerce it is possible to use any user interface to access the data of the online store. It is a significant advantage for companies that can choose the most suitable platforms according to their needs (CMS, DXP, etc.).
- Omnichannel: the product can be purchased anywhere. The customer can complete the purchase from any contact point.
- Increased conversion rate: the ability to offer a consistent, frictionless shopping experience increases the conversion rate.
- Better localization: localization is the cultural adaptation that is made when you have an online store that sells in different countries (description translations, adaptation of products to local culture, etc.). This technology simplifies the creation of different sections for each market.
- Simpler structure: by separating the front end from the back end it is possible to develop and manage the two areas independently, thus simplifying the architecture of the online store.
- Automation: once you have established how content related to a product should be displayed, you can automate this procedure and have different content formatting for each channel.
- Better data acquisition and management: in headless commerce, the software doesn’t depend on the ecommerce itself and therefore can be freely chosen among those most suitable for collecting data on customer purchasing behaviour.
For example, you might choose one provider for the cart, a different one for data acquisition, and another, like ShippyPro, for superior logistics.
- Better performance: in general, headless sites are leaner and therefore faster, more responsive, and easier to update.
But headless commerce does not only have advantages. Here are the downsides of this technology.
- Increased complexity: Headless commerce can be more complex to set up and manage than a traditional architecture. It is not possible to manage it without the intervention of a professional developer.
- Increased dependence on APIs: In headless commerce technology, the software that allows data exchange is API. It is therefore good to structure these exchange systems in the best possible way.
- Higher costs: all of this translates into higher direct and indirect costs for the company.
At the moment, headless commerce is only convenient for big brands that have complex, multi-platform and multi-language websites, that sell on multiple channels and that wish to implement very creative, personalised and cutting-edge solutions.
How to build a headless commerce

Now that we have clarified what a headless commerce is and what the advantages and disadvantages are, let's see how you can implement it, uncovering the steps to take to build your own headless ecommerce structure.
- Choose a backend platform that offers headless functionality for your online store. For smaller businesses, it might be cost-effective to add APIs from a SaaS platform like Shopify Plus, so they don't have to migrate all their infrastructure. A larger company might opt for a fully customised solution for greater flexibility and scalability.
- Choose the right headless CMS: once the headless site is set up, the content management platform must also be implemented in the same way, using headless CMS. What are they? Let's find out more.
CMS (Content Management System) is a software that allows you to manage the content of a website, such as product catalogues, blog articles, site pages and more. Headless CMSs allow you to do the same by separating the back and front ends through APIs. If with a traditional CMS you need multiple platforms to distribute content on different channels, a headless CMS uses a single platform to create optimised content for each channel and distributes it on different touchpoints via API. There are both open-source headless CMS and Software-as-a-service (SaaS) solutions. The former are customizable but complex, the latter are simpler to manage but slightly more limiting.
- Synchronise the APIs with the Headless CMS: the APIs are the engine that moves the whole headless commerce structure, ensuring an easy and smooth data transfer. The best way to do this is to rely on established providers, who offer ready-to-use solutions for headless commerce. This avoids having to use the various plugins needed in traditional ecommerce, that require frequent updates and adjustments. On the contrary, APIs, once set up correctly, require no further changes.
All these steps are complex and must be done gradually, first testing small portions of the website, and then proceeding after having verified that everything works smoothly.
Here is a list of the best headless platforms to use for your ecommerce.
The 8 best headless e-commerce platforms

-
Strapi. It is a headless open-source CMS that is very flexible and offers full control to both developers and users for content management. It is developed in JavaScript and is fully customizable.
-
Shopify. A great solution for businesses of any size looking for flexibility. Shopify Plus, in particular, is able to offer cutting-edge technological solutions and high levels of customization.
-
Contentful. It is a composable content platform, meaning that the contents can be used immediately, regardless of what will be published and where.
-
WooCommerce. It is a very popular platform that also supports headless technology. It is customizable and open source, built on WordPress and is a great solution for small, as well as medium businesses.
-
BigCommerce. It defines itself as the most popular ecommerce solution provider that improves the user experience with the best headless integrations.
-
Salesforce Commerce Cloud. Another platform that supports the headless structure and offers full integration flexibly and reliably.
-
Sanity. It is an open-source platform that allows you to build and manage the backend of an online store in a headless way. It offers a variety of features for content management.
-
Sitecore. It is a composable digital experience platform that integrates everything, from content to ecommerce and is used by brands like L'Oréal and Puma.
Conclusion
In this article we have seen how this new technology can revolutionise the world of ecommerce. We analysed the pros & cons, overviewed the structure and the usable platforms.
However, it is always good to consider every aspect and make sure that the platform you choose is suitable for your business. To be sure of this, it is important to speak to a professional in the field.
Ecommerce statistics show that headless commerce is the future of online commerce and entrepreneurs must keep up to date with the latest trends in an industry that is increasingly embracing omnichannel and social commerce.
Headless commerce FAQs
What does headless commerce mean?
Headless commerce is an ecommerce structured with an innovative technology that allows you to separate the front end (the head) of the online store from the back end where all the data is stored. This architecture, made possible thanks to APIs, offers advantages in terms of development, customization, multi-channel integration and speed.
What are the benefits of headless commerce?
Headless commerce has several advantages, for instance it allows greater flexibility and a complete omnichannel experience. In fact, you can use any user interface and customers can buy products on any channel. This, together with a quick and frictionless shopping experience, increases conversion rate. Other benefits include an improved localization, the automation of different content for each channel and the collection of customer data.
Passionate freelance copywriter, with a niche in ecommerce and logistics. When collaborating with ShippyPro, she loves writing about trends, marketing and communication strategies to help brands gain an edge in an ever-evolving digital landscape.